Have you noticed that more people in your circle are being diagnosed with an autoimmune condition? That’s not surprising. Incidences of this disease have been steadily increasing over the past few years. In fact, according to the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, autoimmune diseases are now the third leading cause of death in the U.S.
There are a lot of theories about why autoimmune disorders are on the rise. Here are a few ideas.
- Our changing environment which now contains more stressors and harmful chemicals makes our immune system work harder.
- Our sedentary lifestyle and unhealthy diet allow toxins to build up in our bodies.
- There aren’t more cases. It’s the increased knowledge about the disease which allows doctors to correctly diagnose it.
Frederick Miller, M.D., scientist emeritus at the Environmental Autoimmunity Group of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), says that people in the U.S. now have a totally different diet, which consists of fast foods, processed foods, and additives. Aside from that, there is also an obesity epidemic as a result of our sedentary lifestyle. And with more than 80,000 chemicals in the country, different patterns of infectious agents have emerged every year.
The environment has also become noisier, which has added more stressors. Stress is known to reduce the immune system’s capacity to fight off antigens.
A recent study found that there are more than 1 million people in the UK who are suffering from an autoimmunity condition – including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and type-1 diabetes mellitus. The number is expected to rise by 50 percent within the next 10 years as the population ages.
Dr. Gala’s Quick Take
Yes, autoimmune disorders are on the rise due to increased exposure to environmental factors and changes in lifestyle and diet. These factors disrupt the immune system, leading to a higher incidence of autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune Disease is More Common in Women, According to Studies
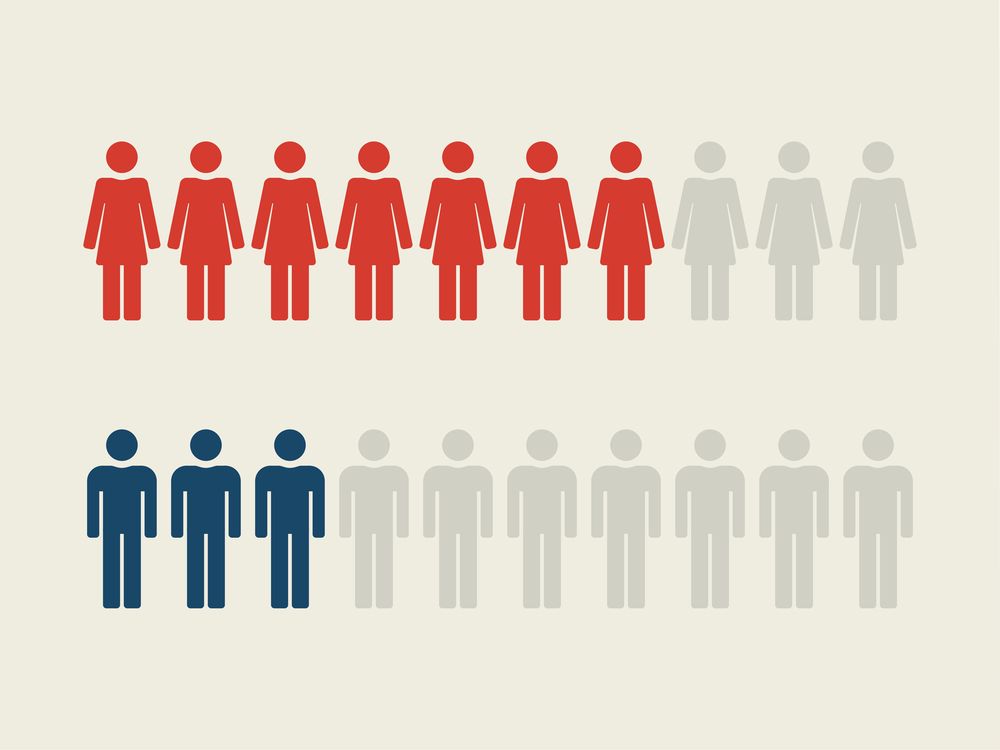
One of the most at-risk groups, when it comes to autoimmune diseases, are women. According to statistics from the American College of Rheumatology, one out of three women will develop some form of autoimmune disorder during their lifetime. This means that about 30% of all Americans have been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease.
According to Southern Hill Hospital, women make up 75 percent of patients with diseases of the immune system. While there are no definitive answers as to why this might be, it is speculated that one of the reasons is that women may have more sophisticated immune responses which contribute to overactivity. Female sex hormones such as estrogen may also influence inflammation.
In fact, other studies also say that women are twice as likely to get certain cancers compared to men because of the decreasing estrogen levels when women reach their mid-40’s. Estrogen helps protect against cancer cells growing inside our bodies. That’s why when we lose too much estrogen, our immune systems start to attack healthy tissue instead of just bad cells.
Women also tend to be affected by autoimmune diseases earlier than men. In fact, according to ACR data, over half of all patients who developed an autoimmune disease before age 40 belong to the female gender. This may be due to hormonal changes during pregnancy or menopause. It could also have something to do with genetics. For example, if one parent had an autoimmune disorder, then their children might inherit this genetic trait.
Women who experience peri-menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, fatigue, and vaginal dryness are also more prone to developing autoimmune diseases. Although these symptoms usually go away after menopause, sometimes they don’t and even become worse over time.
Another factor that contributes to autoimmune diseases among women is stress. Stress causes the hormone, cortisol, to surge through the bloodstream. Cortisol suppresses immunity which makes us susceptible to infections. If we’re constantly stressed, our immune systems won’t work properly.
If you’re experiencing a lot of stress, here are mindfulness practices that you can do to reduce your anxiety and stress naturally.
The Rising Toll of Autoimmune Diseases in Older People

Autoimmune diseases are prominent in young people and are certainly not limited to the elderly. However, the frequency of autoimmunity antibodies increases considerably with advancing age. Recent studies show that autoimmune disease rises significantly when people reach 50 years of age.
There are several reasons why older adults are more prone to developing autoimmune diseases. The first reason is that our immune system function declines as we age. Aged immune cells cannot differentiate between self and non-self (foreign) antigens. The immune system must first recognize its own cells to destroy invaders.
Aging also leads to increased oxidative damage within tissues. Oxidative damage can cause DNA mutations leading to cell death. Lastly, increased inflammation occurs with advanced age. Inflammation damages organs and tissues.
Autoimmune Disease is More Common in Developed Countries
According to a recent epidemiology analysis by GlobalData, the US and the UK, two of the most highly developed countries in the world have a higher prevalence of the autoimmune diseases systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and Sjögren’s syndrome compared to other highly developed countries such as Italy, Germany, and Japan. A 2019 report by Statista showed that the United States ranked highest when it comes to autoimmune diseases, followed by EU-5, China, Brazil, Russia, and Japan. While there are several reasons for this such as population characteristics, scientists are looking at environmental factors as one of the reasons.
The Hygiene Hypothesis
An article by Yolanda Smith, B.Pharm. talks about the “hygiene hypothesis” which suggests that the rise in autoimmune disorders might be caused by changes that occurred in the sanitation standards and practices of industrialized countries. These changes include having a supply of almost sterile water, the use of antibiotics, and vaccination against preventable childhood diseases.

Based on the principle of the hygiene hypothesis, when children are exposed to germs and certain types of infection, their immune system develops. Specifically, it teaches their body to distinguish between harmful and harmless substances. It also teaches the immune system not to overreact.
According to Dr. Debby Hamilton of Researched Nutritionals, since children in developed countries are exposed to less dirt and germs and are exposed to more hand sanitizers, they are more prone to develop allergies and autoimmune diseases later in life.
Changes in Gut Microbiome
The human gut microbiome has been shown to be important for health and disease. According to research by Neuman and Koren, the changes in our gut microbiome are linked to our geographical location, diet, lifestyle, and life stage. A recent study found that the composition of the gut microbiome was different between individuals from developed countries and those from developing countries. This difference may explain why some diseases, including autoimmune diseases, are more common in developed countries.
Environmental Toxins
Environmental toxins such as mercury, lead, arsenic, and pesticides can cause autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and fibromyalgia. These toxins are more abundant in developed countries than in undeveloped ones because industrialization adds chemicals to the environment we are exposed to every day.
Why Autoimmune Disorders are on the Rise: Contributing Factors to Autoimmune Disorder

Sex Genes
Women tend to have higher incidences of autoimmune disease than men. This has been attributed to the difference in sex hormones. Men typically have higher testosterone levels than women. Testosterone stimulates the growth and development of lymphocytes. Lymphocyte activity decreases when testosterone drops below normal levels. The result is less protection from infection.
Genetics
Genetics plays a role in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. The genes that cause these diseases are called HLA genes, which are located on chromosome 6. These genes are responsible for producing proteins that help the immune system identify foreign invaders.
If you are wondering if autoimmune disease is hereditary, read this blog post for more information.
Obesity
The connection between obesity and autoimmune disease may be due to the fact that fat cells produce inflammatory cytokines that cause inflammation in the body.
Smoking and exposure to toxic agents
Smoking is associated with an increased risk for several autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. The mechanism behind these associations is unclear but may be related to the effects of tobacco smoke on immune cells.
Certain medications
Medications such as steroids and immunosuppressants can cause autoimmune diseases. The best way to prevent these conditions is to avoid taking them.
Infections
There is a strong link between infections and autoimmune diseases. The immune system attacks the body’s own tissues when they become infected. Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
Ways to decrease the risk of getting autoimmune diseases

There are a lot of ways to prevent autoimmune disease. If you are highly likely to develop an autoimmune disorder, you should try the following steps to lower your risk:
- Avoid smoking
- Eat well
- Get enough sleep
- Exercise
- Reduce stress
- Drink plenty of quality water
- Maintain good hygiene
- Take care of your mental health
- Seek medical attention if you have any symptoms
- Don’t take certain drugs
- Be aware of environmental toxins
- Have regular checkups
What You Can Do: Taking Care of Your Immune System by Managing Stress
Stress can be a real killer. It can make us sick, slow our metabolism, and even kill us. But there are ways to manage stress so that it doesn’t have such a negative impact on our health.
One of the best ways to take care of our immune system and reduce our risk of developing an autoimmune disorder is to manage our stress levels. Stress has many different causes including work pressures, family problems, financial worries, relationship issues, illness, injury, and more. If you have several unfinished tasks or open loops in these areas, it will contribute a lot to your stress. Managing stress helps keep our bodies in balance and reduces inflammation which plays a role in most autoimmune disorders. Here is a guide on how to close open loops to help you manage stress.
While there are groups of people who are more at risk of developing autoimmune disease, the fact is, that everybody can fall victim to it. This is why no matter what our age, sex, or location is, we must make it a priority to continually improve our immune system.
Fortunately, taking care of our immune system doesn’t require a lot. Doing a few things regularly goes a long way. Those include – eating right, exercising, getting adequate rest, maintaining a positive attitude towards life, and seeking professional advice when necessary. And, yes, work to keep those stress levels low.
“If you came into my office, I’d ask you a lot of questions that would help us connect the dots … so that together we can deal with your toxic stress.
Every situation is unique and you need a plan that works for you. Not a one-size-fits-all solution.
If you’re thinking you can’t come into my office, don’t worry. I’ve created a program with all of my initial recommendations to help you unravel the mystery. You can use it at home and at your convenience.
So if you’re thinking that managing chronic stress just isn’t possible … or even the answer … for you, I want to show you what you may be missing.
And how you can identify the toxic stressors that are creating your symptoms with my Human Energy System Reboot. You can get started HERE.” – Dr. Gala